Search
Biophysics of perception, receptors, vision
Sensory perception. Reflex arc. Local response and Action potencial. Coding of sensory information on Paccinian Corpuscle (a skin receptor for touch and pressure). Coding of Stimulus on paccinian corpuscle. Receptors - Definition and properties. Receptors - Classification. The Flight Reflex. Laws of Sensory Perception. The Law of Adaptation. Receptor Adaptation. Biophysics of Vision. Anatomy of the Eye. Scheme of the Eye. Vitreous body. Retinal Background. COLOR VISION (HELMHOLTZ -YUANG THEORY of Color Vision). MYOPIA (Nearsightedness). Hyperopia - Farsightedness. PRESBYOPIA - OLDSIGHTEDNEES. Refraction Failures - scheme.
Biophysics of Breathing
Anatomy of Breathing. External and Internal Breathing. Respiratory and Cardiovascular Relationships. Ventilation - the role of respiratory muscles. Ventilation - types (in adults). Origine of Breathing. Mechanics of breathing. The Lung Volumes.The Lung Capacities. Morphology of Alveoli and Capillaries (Coupling of respiratorz and Cardiovascular System). Diffusion through the alveolo - capillary membrane. Dynamics of Diffusion.
Biophysics of hearing
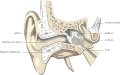
Ear - anatomy. Composition of Inner Ear. Organ of Corti - composition. Mechanism of hearing.
Biophysics of heart and circulation
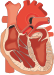
Heart as a source of biopotentials. Heart as a pump. Blood flow in vessels.
Anatomy of Heart. Hearth - Source of Electric Biopotentials. Action Potential of Sinoatrial Node and Prepotential. Spreading of Electric Depolarisation in Heart. Heart as a Pump. Dynamic of Heart. Blood Pressures in Heart. Elasticity of aorta and arteries. Blood Circulation. Blood flow - types. Types of Blood pressures. Measurement of BP. Filtration at Capillary Loop.
Biophysics Of Muscle Contraction
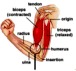
Basic muscle properties,.Sceletal, cardiac, smooth muscles and the differences. Basic muscle and muscle cell structure (myofibril, sarcomere, actin, myosin...). Motor unit, neuro-muscular junction, acetylcholine, end-plate potential. T tubules, sarcoplasmic reticulum, muscle fiber action potential. Muscle contraction and its control (tropomyosin), role of Ca ions and ATP. Single muscle twitch, superposition, summation, tetanus (unfused, fused), rigor mortis. Single unit and multiunit smooth muscle, gap junction, syncytium. Cardiac muscle structure, intercalated discs, Ca induced Ca release. Cardiac muscle action potential, the duration of action potential, summation of contraction.
Biophysics Of Action Potential & Synapse
Depolarization, repolarization, hyperpolarization, action potential – the shape, mechanisms, refractory periods, propagation of action potential (continual spreading, saltatory conduction), electrical stimulation – rheobase, chronaxy, graded potential, synapse, neurotransmitter, mechanisms of transmission receptors (ionotropic vs. metabotropic), EPSP, IPSP, summation (temporal, spatial), convergence, divergence.